
Apple Cider Vinegar for Diabetes: A Natural Remedy or Just a Fad?
In recent years, apple cider vinegar for diabetes (ACV) has gained significant popularity and it is also found as a potential remedy for various other health conditions. While some claim that ACV can help manage blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, others find it perfect to use in cooking.
ACV’s versatility extends beyond its potential benefits for diabetes management, as many individuals find it a flavorful addition to their cooking and salad dressings, adding a tangy and unique twist to their culinary creations.
This article delves into the topic of using apple cider vinegar for diabetes, examining the scientific evidence, benefits, risks, and recommendations for incorporating ACV into a diabetic lifestyle.
Understanding Diabetes
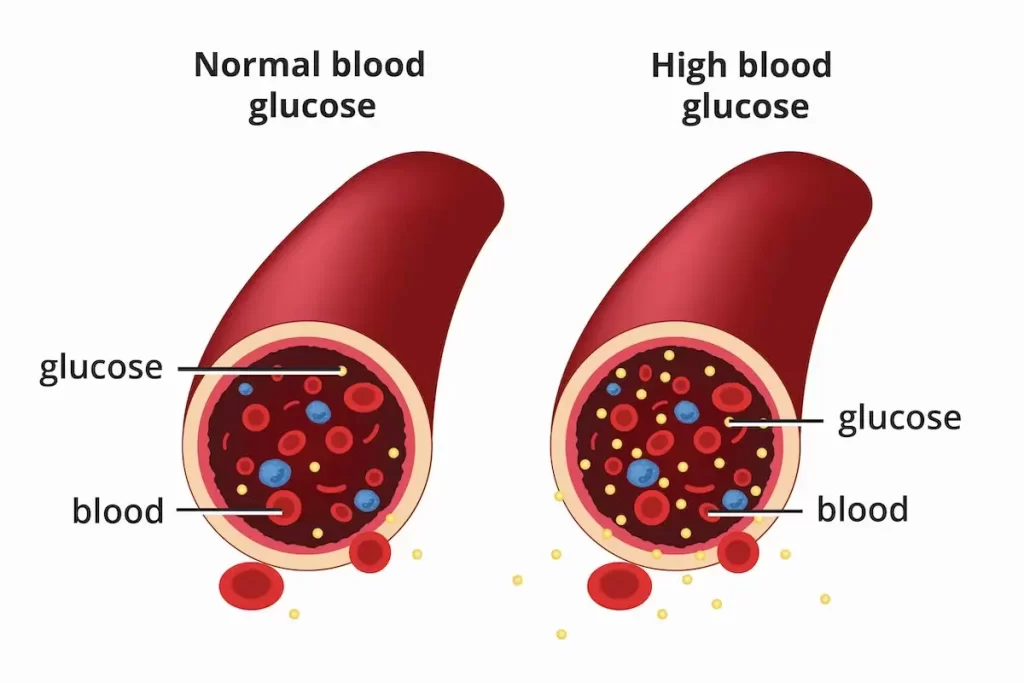
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from either the body’s inability to produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or its ineffective utilization (type 2 diabetes). Maintaining balanced blood glucose levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications and manage their condition effectively.
When it comes to diabetes management, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and monitoring blood sugar levels play a vital role. Additionally, incorporating natural remedies like apple cider vinegar has garnered attention as a potential adjunct therapy for diabetes.
The Apple Cider Vinegar Hype: A Miracle Cure for Diabetes?
In recent years, ACV has gained attention for its potential health benefits, including its supposed ability to aid in diabetes management. Proponents of ACV claim that it can help lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss—all of which are essential aspects of diabetes management.
Unveiling the Scientific Evidence
Does apple cider vinegar for diabetes really help? Here is the evidence.
While anecdotal reports and testimonials have contributed to the popularity of ACV as a diabetes remedy, scientific research on its effectiveness remains limited. Some studies have suggested potential benefits, while others have found to do more research and studies.
Blood Sugar Control: Several small-scale studies have shown that consuming apple cider vinegar before a meal can help lower post-meal blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. ACV’s acetic acid is believed to slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, leading to a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Insulin Sensitivity: Some research indicates that ACV may enhance insulin sensitivity, potentially aiding in the management of type 2 diabetes. However, further large-scale studies are needed to establish this relationship definitively.
Weight Management: Obesity is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Some studies suggest that apple cider vinegar may contribute to weight loss by increasing feelings of fullness and reducing calorie intake. However, the evidence is limited, and more research is required to understand the direct impact of ACV on weight management.
Apple Cider Vinegar for Diabetes : Considerations and Risks
Before incorporating ACV into a diabetes management routine, it is crucial to consider potential risks and limitations associated with its usage.
Acidic Nature: ACV is highly acidic and can erode tooth enamel and irritate the digestive tract. To minimize these effects, it is advisable to dilute ACV with water or consume it as part of a meal. Furthermore, drinking ACV through a straw and rinsing the mouth with water afterward can also help protect tooth enamel from the acidic effects.
Medication Interactions: If you are taking medication to manage your diabetes, consult with your healthcare provider before adding ACV to your regimen. ACV has the potential to interact with certain medications, such as insulin and diuretics, leading to adverse effects.
Individual Variations: Each person’s response to ACV may vary, and what works for one individual may not work for another. Monitoring blood sugar levels closely is crucial when introducing apple cider vinegar for diabetes into your routine.
Incorporating Apple Cider Vinegar into a Diabetic Lifestyle
If you decide to try ACV to complement your diabetes management, consider the following recommendations:

Start Slowly: Begin with small amounts of apple cider vinegar for diabetes, such as one to two teaspoons per day and gradually increase the dosage if well-tolerated. This allows your body to adjust and minimize any potential side effects.
Dilute with Water: To protect your tooth enamel and digestive system, mix ACV with water before consuming. A common ratio is one to two tablespoons of ACV in a glass of water.
Timing Matters: Some research suggests that consuming ACV before a meal may help with blood sugar control. However, individual responses may vary. Monitor your blood sugar levels carefully after consuming ACV to understand how it affects your body.
Regular Monitoring: It is crucial to monitor your blood sugar levels consistently when using ACV. Keep a record of your readings before and after incorporating ACV into your routine. This will help you gauge its impact and make any necessary adjustments.
Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before making any significant changes to your diabetes management plan, consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health needs, medication regimen, and overall diabetes management goals.
As research in apple cider vinegar for diabetes continues, it is essential to stay informed about the latest scientific findings and recommendations. Diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and consistent monitoring. Working closely with healthcare professionals will ensure that you make informed decisions to effectively manage your diabetes and maintain overall well-being.
Conclusion
In the realm of alternative therapies for diabetes management, apple cider vinegar for diabetes has gained attention for its potential benefits. While there is some scientific evidence suggesting that ACV may help with blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity, further research is needed to establish its efficacy definitively.
Moreover, it is crucial to consider the risks and limitations associated with ACV usages, such as its acidic nature and potential interactions with medications.
If you are considering incorporating apple cider vinegar for diabetes management, proceed with caution and consult with your healthcare provider. ACV should not replace standard diabetes medications or prescribed treatment plans but may serve as a complementary approach.
